Perforated steel sheet is a versatile material extensively used in the construction industry due to its unique properties and applications. Made from steel and featuring a series of holes, this material combines the strength and durability of traditional steel with enhanced functionality. Builders and architects increasingly turn to perforated steel sheets for various projects, as they offer both aesthetic appeal and practical solutions for a wide range of construction needs.
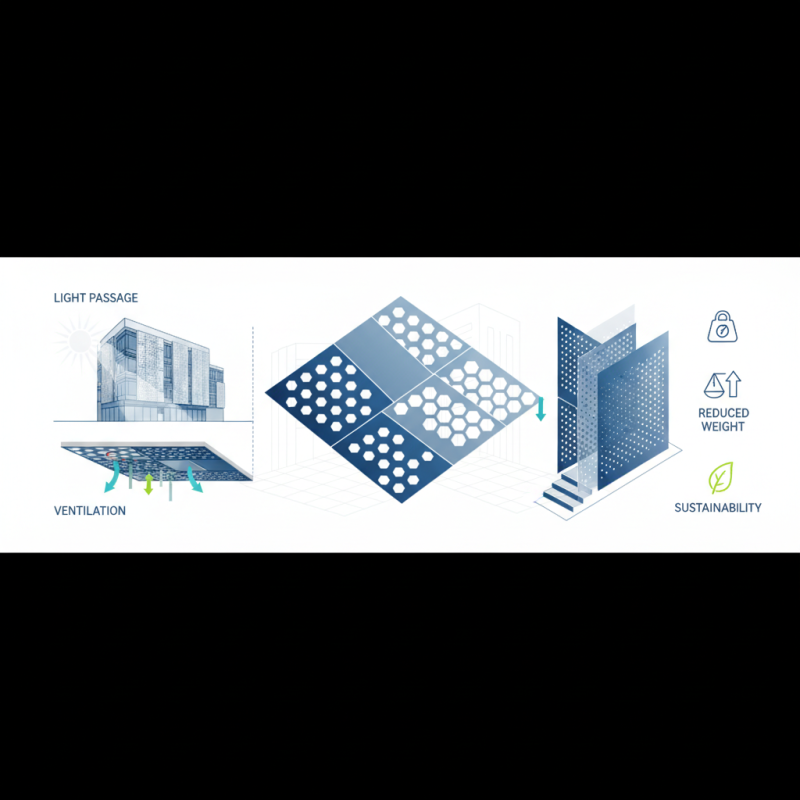
In construction, perforated steel sheets serve multiple purposes, from providing structural support to facilitating ventilation and light passage. These sheets can be utilized in facades, ceilings, and partitions, allowing for creative designs that do not compromise on safety or functionality. Additionally, their ability to regulate airflow and reduce weight makes them an excellent choice for modern building practices focused on sustainability and efficiency. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the significance of perforated steel sheets is poised to grow, further establishing their role as a crucial component in contemporary architectural designs.
Perforated steel sheet is a versatile material widely used in construction due to its unique properties. Defined as a flat sheet of steel that has been punched or drilled with a pattern of holes, it offers a combination of strength and aesthetic appeal. The characteristics of perforated steel sheets make them suitable for various applications, including facades, flooring, and fencing. The holes can vary in size, shape, and spacing, allowing for customizable designs that meet specific architectural and engineering requirements.
One of the key characteristics of perforated steel sheet is its ability to provide ventilation and light while maintaining structural integrity. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications such as ventilation grills and sound barriers, where airflow and noise reduction are essential. Moreover, the open design allows for reduced weight compared to solid metal sheets, making them easier to handle and install. In addition, their corrosion resistance, when treated properly, enhances their durability, enabling them to withstand harsh environments commonly found in construction settings. This combination of functionality and aesthetic versatility underscores the increasing popularity of perforated steel sheets in modern architectural design.
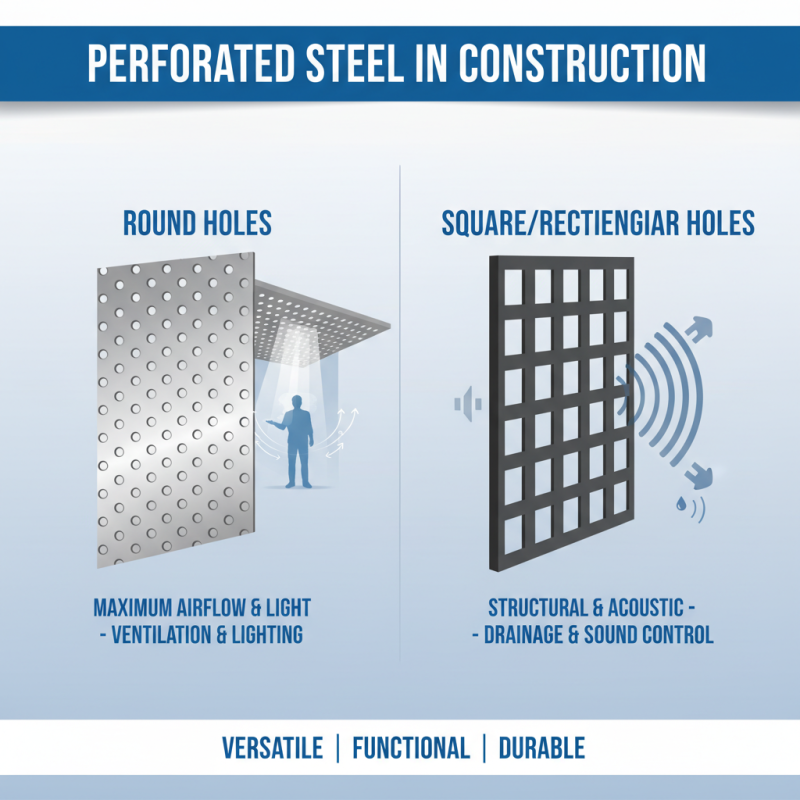
Perforated steel sheets are commonly utilized in construction due to their versatility and functionality. The types of perforations in these sheets vary widely, each serving distinct purposes that enhance their usability in different applications. Standard round holes are frequently used for maximum airflow and light penetration, making them ideal for applications in ventilation and lighting fixtures. In contrast, square or rectangular perforations may offer more structural integrity while still allowing for drainage or acoustic control, making them suitable for environments where sound reduction is essential.
Furthermore, the size and pattern of the perforations can greatly influence the performance of the steel sheet in specific contexts. Larger holes may provide better drainage in areas prone to water accumulation, while smaller, tightly spaced perforations can enhance the aesthetic appeal of architectural facades while maintaining structural strength. Additionally, custom perforation patterns can be designed to meet specific design criteria, blending functionality with aesthetic considerations. This adaptability ensures that perforated steel sheets are not only functional but also contribute to the overall design of construction projects.

Perforated steel sheets are increasingly becoming a staple in construction due to their versatility and functional benefits. These sheets are created by puncturing holes into the steel, offering unique properties like reduced weight and enhanced aesthetics. Their common applications in construction include architectural facades, noise barriers, ceiling tiles, and even screening systems for ventilation and lighting. According to a report by Technavio, the global market for perforated metal is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 5% from 2021 to 2025, showcasing the material's rising prominence in various sectors, including construction.
One significant application of perforated steel sheets is in architectural designs, where they provide both functionality and visual appeal. Architects utilize these sheets for cladding and sun shading, allowing natural light to filter through while maintaining structural integrity and privacy. Additionally, their use in acoustic walls is growing, as they are effective in noise reduction while still appearing modern and sleek. The construction industry has recognized that enhancing both aesthetic and functional aspects of buildings is crucial, making perforated steel an ideal choice.
Tips for contractors considering perforated steel sheets include evaluating the material's thickness and hole size based on the specific application to ensure maximum effectiveness. It's also recommended to consult with structural engineers to determine the load-bearing capacities and any required treatments for corrosion resistance. Lastly, always consider local building codes and regulations when incorporating perforated sheets into construction designs to ensure compliance and safety standards are met.
Perforated steel sheets have emerged as a versatile element in architectural design, offering a unique combination of aesthetic appeal and functional advantages. The numerous holes in the sheet not only create visually striking patterns but also allow for the manipulation of light and airflow. This property is particularly beneficial in enhancing natural ventilation within buildings, reducing reliance on artificial climate control systems. Architects often utilize perforated steel to create facades that balance between solid and void, giving structures a dynamic presence that changes with the viewer's perspective.
Additionally, the use of perforated steel in construction contributes to sustainability goals. Due to its lightweight nature, perforated steel can reduce material costs and overall structural weight, which in turn decreases the energy required for transportation and installation. The sheets can be easily fabricated to fit various design needs, making them a practical choice for both new constructions and renovations. With the ability to integrate into various applications, from sunshades to safety barriers, perforated steel not only supports innovative design solutions but also fosters a more environmentally conscious approach in architectural projects.
When installing perforated steel sheets, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. First, the selection of the appropriate type of perforated steel sheet is crucial, as different applications may require varying sizes of holes and thicknesses. Installation should be performed on a level surface, with careful attention paid to structural support. Fasteners and mounting techniques must be chosen based on the sheet’s intended use, aesthetic preferences, and environmental conditions. Adequate spacing and alignment are essential to prevent warping or bending during installation.
Maintenance of perforated steel sheets involves regular inspections to identify signs of wear or corrosion. Cleaning the sheets periodically with non-abrasive cleaners can help maintain their appearance and structural integrity. In environments prone to moisture or salt exposure, applying protective coatings may be beneficial to prevent rust formation. It's also advisable to check for any loose fasteners or structural damage that could compromise the sheet's functionality. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities can help in planning future inspections and upkeep, ultimately extending the lifespan of the installation.






