Perforated Steel Sheets are increasingly vital in various industries. Known for their strength and versatility, these sheets feature holes that enhance functionality. John Anderson, a materials expert, once remarked, "Perforated Steel Sheets bring both aesthetic appeal and practical advantages."
This unique material finds use in construction, filtration, and decor. In buildings, it provides structural support while allowing airflow. In the filter industry, it plays a crucial role in separating materials. However, it is essential to choose the right perforation size and pattern for specific applications; this can sometimes be a challenging task.
While professionals highly value Perforated Steel Sheets, not all applications are straightforward. Each project's requirements may lead to unexpected complications. Understanding how to effectively utilize this material is crucial for achieving optimal results. Each decision can significantly impact both performance and aesthetics.

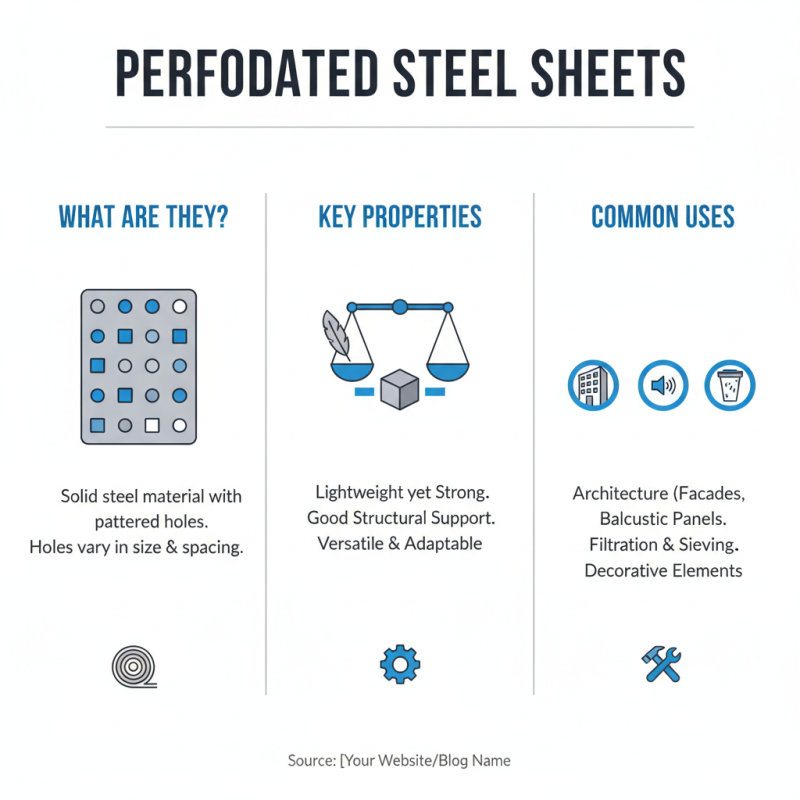
Perforated steel sheets are versatile materials with numerous applications. They are made from solid steel, but feature a pattern of holes. These holes can vary in size and spacing, allowing for different functional and aesthetic properties. Such sheets are lightweight yet strong, providing good structural support.
The characteristics of perforated steel sheets offer unique advantages. Their open nature allows for airflow, making them ideal for ventilation systems. They can also be used in architectural designs, creating eye-catching facades. The holes can reduce weight, but they might also compromise the material's strength in specific situations. It's essential to consider these factors during design or construction.
Moreover, the aesthetic potential of perforated sheets is remarkable. They can create intriguing visual effects when used in interior design. However, maintenance can be a challenge. Dirt and debris can accumulate in the holes, requiring regular cleaning. This aspect may deter some users from fully utilizing their potential. Understanding both their strengths and limitations is key to maximizing their benefits.
The manufacturing process of perforated steel sheets begins with selecting high-quality steel sheets. These sheets undergo a series of precise operations. First, they are cleaned to remove contaminants. This ensures better adhesion during the perforation phase.
Next, a punching machine is used to create holes in the steel. The size, shape, and spacing of these holes can vary widely. According to a recent report, nearly 70% of manufacturers customize the hole patterns to meet specific client needs. This flexibility allows for a variety of applications, from architectural design to industrial uses.
Once punched, the sheets may undergo additional treatments. Techniques like galvanizing or powder coating can enhance durability. Reports indicate that treated perforated sheets last up to 50% longer in harsh environments. However, improper treatment can lead to rapid corrosion. Manufacturers must ensure every step is completed correctly to avoid costly failures. Each process stage is crucial for achieving high-quality end products.

Perforated steel sheets are widely used in various industries due to their versatile features. The mining and construction sectors frequently utilize these sheets for filtration and ventilation. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global demand for perforated metals is projected to grow by 5.3% annually. This reflects the increasing reliance on these materials in structural applications.
In the automotive industry, perforated steel sheets serve critical roles. They are commonly found in vehicle grills and exhaust systems. Their ability to allow airflow while providing necessary strength is vital for vehicle efficiency. The automotive sector alone accounts for about 30% of the total perforated sheet market. However, challenges arise in ensuring uniform perforation sizes. Sloppy manufacturing can lead to inconsistent performance.
Architectural applications also leverage perforated steel sheets extensively. They are often used in building facades and interior design elements. A report by Research and Markets indicates a rising trend in decorative panels. The aesthetic value combined with functionality makes them popular. Still, designers sometimes overlook the balance between practicality and appearance. This can lead to costly renovations when initial choices do not align with structural needs.
Perforated steel sheets are widely recognized for their versatility and strength. They consist of steel panels with a series of holes punched through them, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal. One significant advantage of using these sheets is their ability to provide ventilation and light transmission. This feature makes them ideal for applications in architecture, where airflow is essential.
Another benefit is the material's durability. Perforated steel sheets can withstand harsh conditions. They resist corrosion, which adds to their longevity. Additionally, they are lightweight, making transportation easier. This is crucial for construction projects that demand quick assembly and installation. The sheets also require less material than solid steel, promoting sustainability.
Despite their advantages, some challenges exist. The manufacturing process can lead to defects if not properly managed. Holes may be misaligned or uneven, affecting performance and aesthetics. It's vital to choose high-quality materials and manufacturers carefully to mitigate these issues. Balancing cost and quality is a constant concern in the industry, prompting ongoing discussions and improvements.
Perforated steel sheets are known for their unique combination of strength and functionality. Their maintenance is crucial for optimal longevity. Regular inspections help to detect any signs of wear or corrosion. It’s a simple practice that can prevent costly replacements. Data from various industry reports suggest that well-maintained perforated steel can last up to several decades.
Cleaning is essential. Dust and grime can accumulate over time, especially in industrial environments. Using a mild detergent with a soft brush can protect the finish. Many manufacturers recommend this approach. However, some people neglect this step, thinking it’s unnecessary. This oversight can lead to rust and deterioration.
Tips: Ensure that there are no sharp edges on the perforated sheets. Sharp edges can lead to injuries and require extra maintenance. Consider using a coating for added protection against the elements. This can enhance durability.
In environments with extreme exposure, more frequent maintenance is advisable. Some studies highlight that neglect can reduce lifespan by up to 50%. Proper care equips perforated steel sheets to withstand challenges, but it requires effort. Are you doing enough to maintain yours?






