Choosing the right perforated metal sheet for your project can significantly impact both functionality and aesthetics. According to industry expert John Smith, a leading figure in architectural metal design, “The right perforated metal sheet not only meets the technical requirements of a project but also enhances its visual appeal.” Understanding the various aspects of perforated metal sheets, such as hole size, pattern, and material, is crucial for architects, engineers, and designers alike.
When embarking on a project that involves perforated metal sheets, considerations must encompass the application, location, and environmental factors. Whether used for facades, ceiling panels, or filtration systems, the selection process can determine the overall effectiveness of the design. With countless options available, from varying hole diameters to different metal types, making an informed choice ensures that the final product aligns with both practical needs and aesthetic goals. By exploring expert insights and best practices, project stakeholders can navigate the intricacies of perforated metal sheets with confidence.

When selecting the right perforated metal sheet for your project, it's essential to understand its specifications to ensure it meets your design and functional needs. Perforated metal sheets are available in various materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel, each offering distinct properties that influence durability, weight, and corrosion resistance. According to the Metal Industries 2022 Market Report, the demand for aluminum perforated sheets has surged by 18% over the past year, driven by their lightweight nature and aesthetic appeal in architectural applications.
The hole size, spacing, and pattern of perforation are critical specifications that impact both performance and appearance. Common hole diameters range from 1/16 inch to 1 inch, while the spacing between holes can vary significantly based on the desired airflow or light penetration. The perforation percentage, which indicates the ratio of the hole area to the total sheet area, typically ranges from 5% to 50%. A recent industry analysis found that sheets with a perforation percentage of around 30% are most favored for applications requiring a balance between structural integrity and ventilation. Understanding these specifications allows engineers and designers to make informed choices tailored to specific project requirements.

When evaluating material types for perforated metal sheets, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, weight, and corrosion resistance, which can significantly impact performance in unique applications. Common choices include aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it a popular option for exterior applications, such as architectural facades or outdoor furniture. Conversely, stainless steel provides exceptional strength and resistance to staining, which is ideal for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
In addition to metal types, the thickness and perforation pattern also play a critical role in the selection process. Thicker sheets generally offer more strength and durability, while thinner sheets provide flexibility and ease of fabrication. The perforation pattern can affect airflow, light transmission, and aesthetic appeal. For example, circular holes might be ideal for applications requiring unobstructed airflow, whereas decorative patterns can enhance product aesthetics in retail environments. Therefore, carefully evaluating these material characteristics will ensure the right choice for your perforated metal sheet project, leading to better performance and longevity.
When selecting the right perforated metal sheet for a project, determining the appropriate hole sizes and patterns is crucial for ensuring functionality. According to industry reports, the size of the holes significantly impacts airflow, acoustics, and structural integrity. A study conducted by the Metal Construction Association indicates that larger holes (greater than 1 inch) allow for improved ventilation and drainage, making them ideal for applications in the construction and architectural sectors. Conversely, smaller holes (less than 1 inch) are often favored in applications requiring noise reduction or aesthetic appeal, particularly in urban environments.
When deciding on hole patterns, consider how they will affect material strength and performance. For instance, staggered patterns may enhance load-bearing capabilities compared to aligned holes, as they provide more even stress distribution. A report by the American Institute of Steel Construction suggests that customized patterns can also improve processing efficiency and reduce waste, as they can be tailored to specific manufacturing needs.
Tips: Always assess the environmental conditions where the perforated metal sheet will be used. In corrosive environments, a coating or finish may be necessary to protect the material. Additionally, experiment with different patterns and hole sizes through prototypes to visualize how they perform under real-world conditions before finalizing your design.
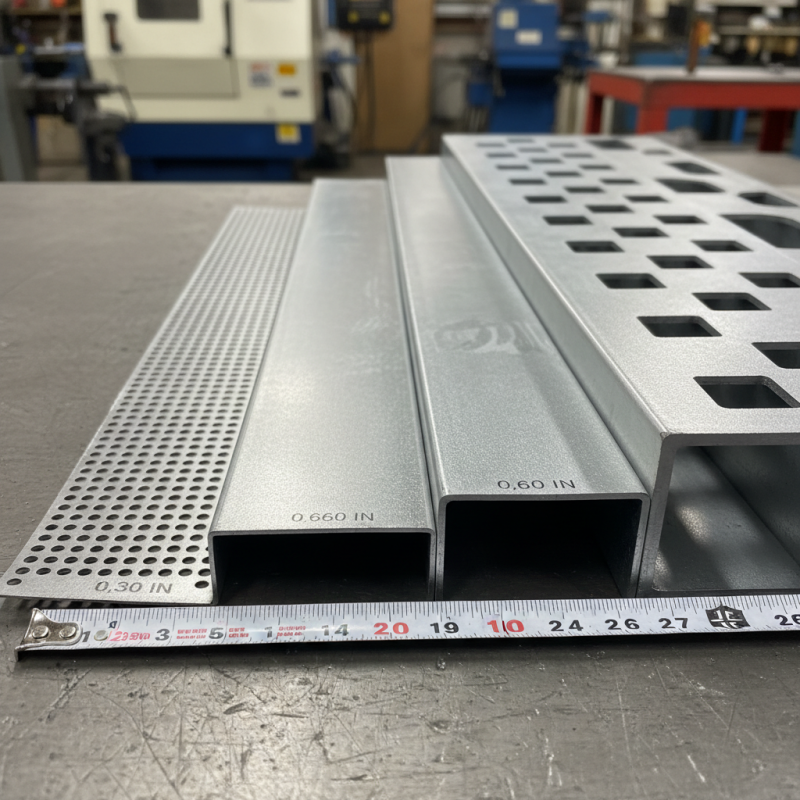
When selecting the right perforated metal sheet for your project, assessing thickness and strength is crucial. The thickness of the sheet often determines its load-bearing capacity and durability. According to a report by MetalSupermarkets, perforated sheets typically range from 0.030 inches to 0.125 inches in thickness, with heavier gauges providing greater strength suitable for structural applications. Consider the expected loads in your design—if your project involves significant weight or stress, opting for a thicker sheet can prevent deformation and enhance long-term performance.
Moreover, the strength of the perforated metal must align with the specific requirements of your application. Factors such as the type of material, hole size, and pattern can significantly impact the mechanical properties. For instance, a study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) indicates that sheets with smaller perforations and minimized spacing often exhibit increased stiffness and better stress distribution. It's essential to balance aesthetic choices with functional capabilities; while larger holes can enhance airflow and reduce weight, they may compromise structural integrity under certain conditions. Understanding these parameters can help you select a perforated metal sheet that is both visually appealing and appropriately robust for your project.
When selecting perforated metal sheets for your project, the finish and coating options play a critical role in ensuring durability and longevity. The choice of finish not only impacts the aesthetic appeal but also influences the metal's resistance to environmental factors. Common finishes include powder coating, anodizing, and galvanization, each offering unique protective qualities.
Powder coating, for instance, creates a hard finish that stands up well to scratches and is resistant to fading, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Anodizing, typically used for aluminum surfaces, enhances corrosion resistance and allows for vibrant color options.
Coating the metal sheet further enhances its performance by providing an additional barrier against harsh conditions. Various coatings, such as epoxy or polyurethane, can be applied depending on the specific environment in which the metal will be utilized. For projects exposed to moisture or chemicals, a robust coating can prevent degradation and extend the lifespan of the material.
Additionally, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your project, such as exposure to UV light or industrial contaminants, to ensure that the chosen finish and coating will meet the intended use while maintaining both functionality and appearance.