Decorative Expanded Metal is making waves in design and architecture. This innovative material combines strength with an artistic touch. Its unique patterns are not just visually appealing, but also functional.
Many industries are discovering the versatility of Decorative Expanded Metal. It can enhance both aesthetic and structural aspects of a project. From fencing to interior accents, its applications are vast. However, not all uses are perfect. Some designs may not suit every environment, leading to mismatches.
As we explore the best applications and benefits of Decorative Expanded Metal, it is essential to recognize its limitations too. Understanding where it excels and where it falters can lead to smarter choices. Embracing its potential while learning from missteps is crucial for designers and builders.
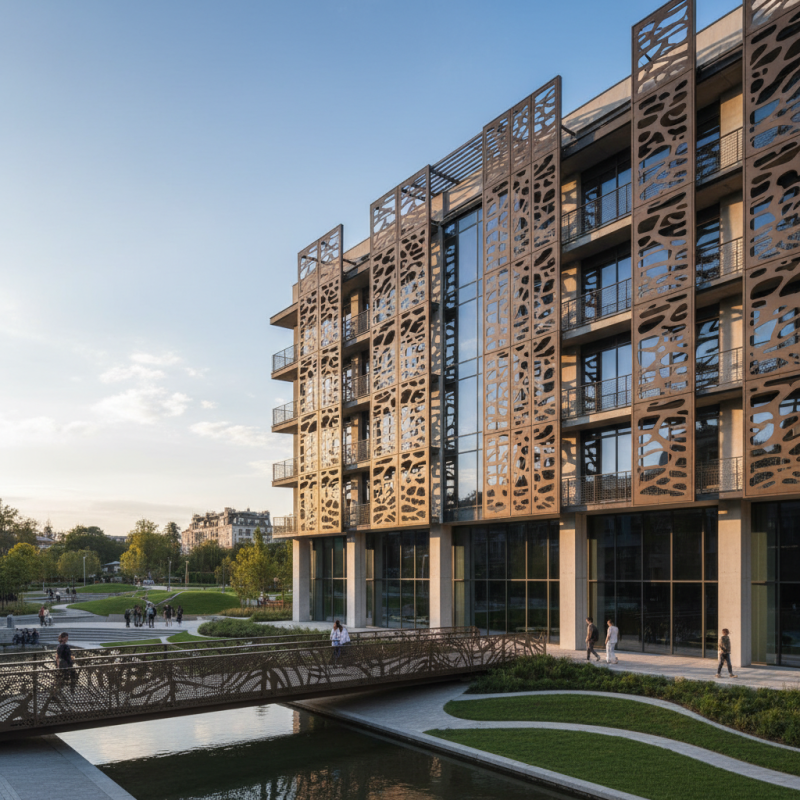

Decorative expanded metal has gained notable popularity in architecture and design. Its unique patterns add character and depth to various spaces. Architects often use it in facades, railings, and partitions. The open structure allows for light diffusion, which creates interesting shadows and effects.
In residential settings, this material provides both aesthetics and functionality. A decorative screen can offer privacy while enhancing visual appeal. It's versatile, fitting well in both modern and traditional designs. Moreover, its durability ensures that it stands the test of time, though its installation can be tricky.
Some designs may require frequent maintenance to keep them looking fresh. The choice of finish may not suit every environment. Careful consideration is necessary here, as the wrong selection could diminish the overall effect. Ultimately, decorative expanded metal can elevate a space, but thoughtful application and planning are essential for the best outcomes.
This chart illustrates the various applications of decorative expanded metal in 2026, showcasing their prominence in fields such as architecture and design.

Expanded metal has become a key player in decorative applications across various industries. Its design flexibility allows for intricate patterns that enhance aesthetic appeal. According to a recent industry report, the use of expanded metal in architecture is projected to grow by 15% over the next five years. The unique mesh structure provides both decorative and functional benefits, making it a popular material choice among designers.
One of the primary advantages of expanded metal is its lightweight nature. This feature facilitates easier handling and installation. Additionally, it is resistant to corrosion and rust, contributing to a longer lifespan in outdoor applications. Data indicates that projects incorporating expanded metal see a 20% reduction in maintenance costs over their lifetime. The open design allows for enhanced airflow and light penetration, which can create visually striking interior spaces. However, achieving the perfect balance between aesthetic and functionality requires careful planning.
Despite its benefits, there are challenges in using expanded metal. The manufacturing process must be precise to ensure consistent quality. Variability in patterns may lead to inconsistencies in design. Some designers may struggle to visualize their concepts with this material. Addressing these issues can result in a more successful application.
The decorative expanded metal market is experiencing significant growth. In 2026, architectural designs are driving demand for unique patterns. This trend blends functionality and aesthetics seamlessly. Many industries are exploring creative applications. From stunning facades to elegant interior screens, the possibilities are endless.
Sustainability plays a critical role in market trends. Consumers favor eco-friendly materials in their projects. However, sourcing sustainable options can be challenging. Not every supplier meets these requirements, leaving gaps in the market. Designers must navigate these constraints while aiming for innovation.
Emerging technologies are also influencing production techniques. Automation enhances precision but raises questions about handmade craftsmanship. Many artisans worry about losing their touch in a digital world. Balancing technological advances with traditional methods becomes essential. This reflects a broader industry challenge as it moves toward the future.
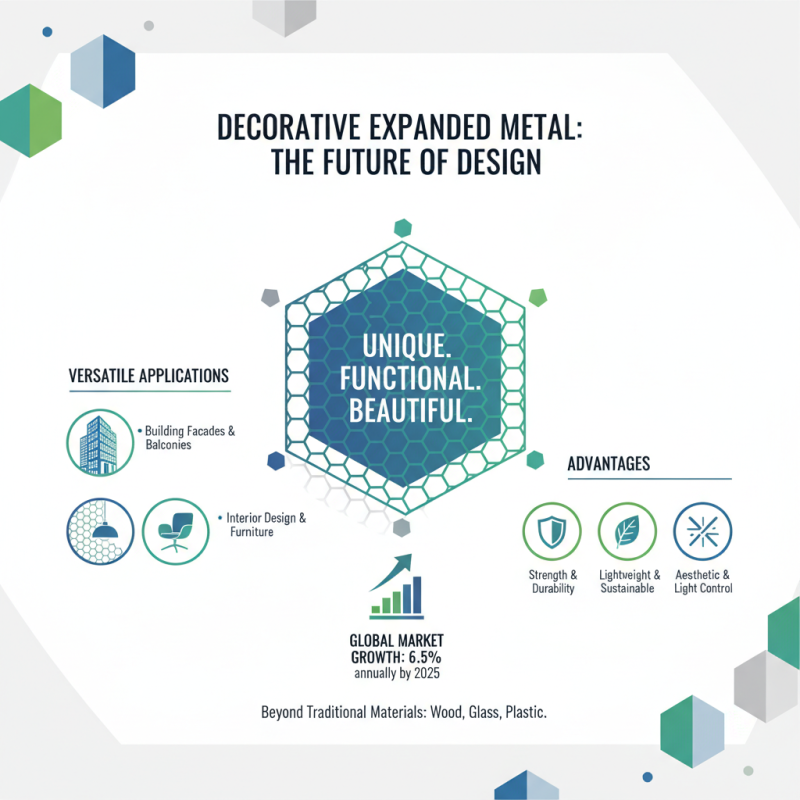
Decorative expanded metal has gained popularity for various applications. It stands as a unique option compared to traditional materials such as wood, glass, and plastic. According to industry reports, the global expanded metal market is projected to grow at a rate of 6.5% annually through 2025. This growth signals a strong preference for materials that provide both function and aesthetic appeal.
When we compare expanded metal to other decorative materials, notable advantages emerge. Expanded metal allows for greater airflow and light penetration, unlike solid materials. Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of designs. This material can be used in arts, architecture, and furniture, adding a modern touch. However, challenges exist. Expanded metal may not always offer the same insulation properties as plastic or wood.
In terms of cost, expanded metal generally falls in the mid-range market. While it might be more expensive than basic plastic, it is usually less than premium wood. This pricing dynamic can limit its appeal to budget-conscious projects. Even with its growing popularity, some architects and designers remain hesitant. They question its long-term durability and maintenance requirements in certain environments.
Expanded metal is a versatile material, widely used for decorative purposes. Its unique design allows for both aesthetics and functionality. The open spaces in its structure can create stunning visual effects while maintaining strength and durability. This duality makes expanded metal an appealing choice for various applications, from architectural facades to garden trellises.
When evaluating the environmental impact of expanded metal, its sustainability comes into focus. Made from recyclable materials, it promotes a circular economy. Using expanded metal can reduce waste, as it produces minimal scrap during manufacturing. However, the energy required for production should be considered. The long lifespan of expanded metal also reduces the need for frequent replacements, leading to lower resource consumption over time. While there are benefits, careful thought is needed regarding its sourcing and production methods. Balancing aesthetics with environmental responsibility is essential in today's world.
| Application | Benefits | Sustainability Impact | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural Facades | Aesthetically pleasing, lightweight | Recyclable material, reduces resource consumption | Long-lasting with minimal maintenance |
| Safety Barriers | High visibility, prevents unauthorized access | Uses less material for effective barriers | Resistant to weathering and corrosion |
| Furniture Design | Unique design possibilities, enhances aesthetics | Sourced from recycled metals, eco-friendly | Robust structure, withstands daily use |
| Industrial Applications | Enhanced ventilation, lightweight construction | Minimizes waste through efficient manufacturing | Durable under demanding conditions |
| Decorative Screens | Customizable designs, artistic expression | Local sourcing reduces transportation impact | Powerful resistance to deformation |






